In the vast and diverse realm of geology, the term metallic stone may not be as straightforward as it seems. It is a term that encompasses a wide range of minerals and rocks with metallic properties. This article aims to delve into the intricacies of metallic stones, their formation, characteristics, uses, and the latest advancements in their study.
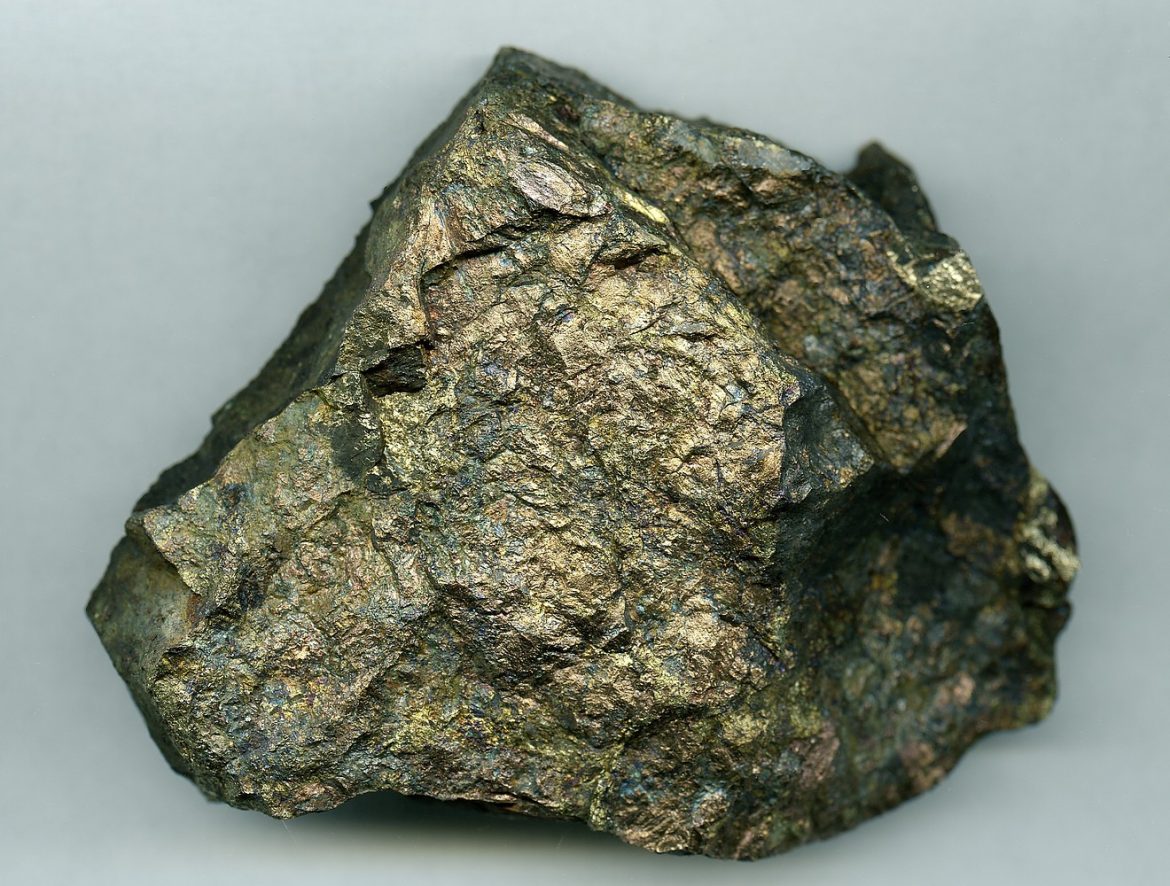
The term metallic stone is often used to describe minerals that possess a metallic luster, a property that refers to the way light interacts with the surface of a mineral. This luster is common in many ore minerals. Pyrite, also known as fool's gold, hematite, magnetite, and galena are all examples of metallic stones.
The formation of these metallic stones is a fascinating process that involves various geological phenomena. For instance, Pyrite forms in hydrothermal veins, sedimentary rocks, and metamorphic rocks. On the other hand, hematite, an iron oxide, forms in soils and sediments through weathering.
The characteristics of metallic stones are as diverse as their types. They are usually opaque and reflective, much like metal. Their hardness varies significantly, with pyrite having a hardness of 6-6.5 on the Mohs scale, while hematite has a hardness of 5-6.
Metallic stones have a wide range of uses in various industries. They are crucial in the manufacturing sector, especially in the production of automobiles, appliances, and industrial equipment. For instance, hematite is a primary source of iron, which is a critical component in steel manufacturing.
In the jewelry industry, metallic stones like pyrite are often used for their unique aesthetic appeal. Despite not being precious metals, these stones offer a distinctive look that appeals to a niche market.
The study and exploration of metallic stones have seen significant advancements in recent years. Advanced imaging technologies have enabled geologists to study these stones at a microscopic level, revealing intricate details about their structure and formation.
Moreover, the advent of space exploration has opened up new frontiers in the study of metallic stones. NASA's Mars Rover, for instance, has discovered high levels of hematite on Mars, indicating the presence of water in the past.
In conclusion, metallic stones are more than just shiny rocks. They are a testament to the planet's dynamic geological history, playing a crucial role in various industries and continuing to intrigue scientists with their complexity. As our understanding of these stones deepens, we can look forward to more exciting discoveries and applications in the future.